Introduction: The Two Sum is a well-known challenge on online coding platforms (Link) where the sum of two elements of a given array need to be equal to a given target integer.
Approach: In multiple ways, this challenge can be solved. One way is to run two loops (nested) and check if any two values of the iterated array sum up to the target, and finally return the indices of those two elements. The program below shows Two Sum in Swift using two loops and variables:
import Foundation
class Solution {
func twoSum(_ nums: [Int], _ target: Int) -> [Int] {
let size = nums.count
for num in 0 ..< size {
for next in num + 1 ..< size {
if nums[num] + nums[next] == target {
return [num, next] }
}
}
return []
}
}
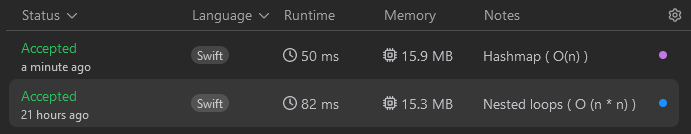
Time Complexity: n2 ;[n equals to the number of elements]
Optimized Approach: Using a Hashmap (also known as Hash table or dictionary in Swift), this challenge can be solved by calculating if the result of reducing one element from the target exists in the given array. It significantly reduces the runtime. An optimized solution of the Two Sum challenge using Hashmap in Swift is written below:
import Foundation
class Solution {
func twoSum(_ nums: [Int], _ target: Int) -> [Int] {
var hashmap = [Int: Int]()
var size = nums.count
for i in 0 ..< size {
var remainder = target – nums[i]
if hashmap.keys.contains(remainder) {
return [i, hashmap[remainder]!]
} else {
hashmap[nums[i]] = i
}
}
return []
}
}
Time Complexity: O(n)
So, using Hashmap (also known as Hash table or dictionary in Swift) rather than nested loops significantly reduces the runtime from O(n*n) to O(n).